Transitions Online_Around the Bloc-The Kremlin’s New Darling: Cryptocurrency
Putin adviser launches bitcoin mining company as Russia pushes alternatives to American dollar.
More...We kindly inform you that, as long as the subject affiliation of our 300.000+ articles is in progress, you might get unsufficient or no results on your third level or second level search. In this case, please broaden your search criteria.

Putin adviser launches bitcoin mining company as Russia pushes alternatives to American dollar.
More...
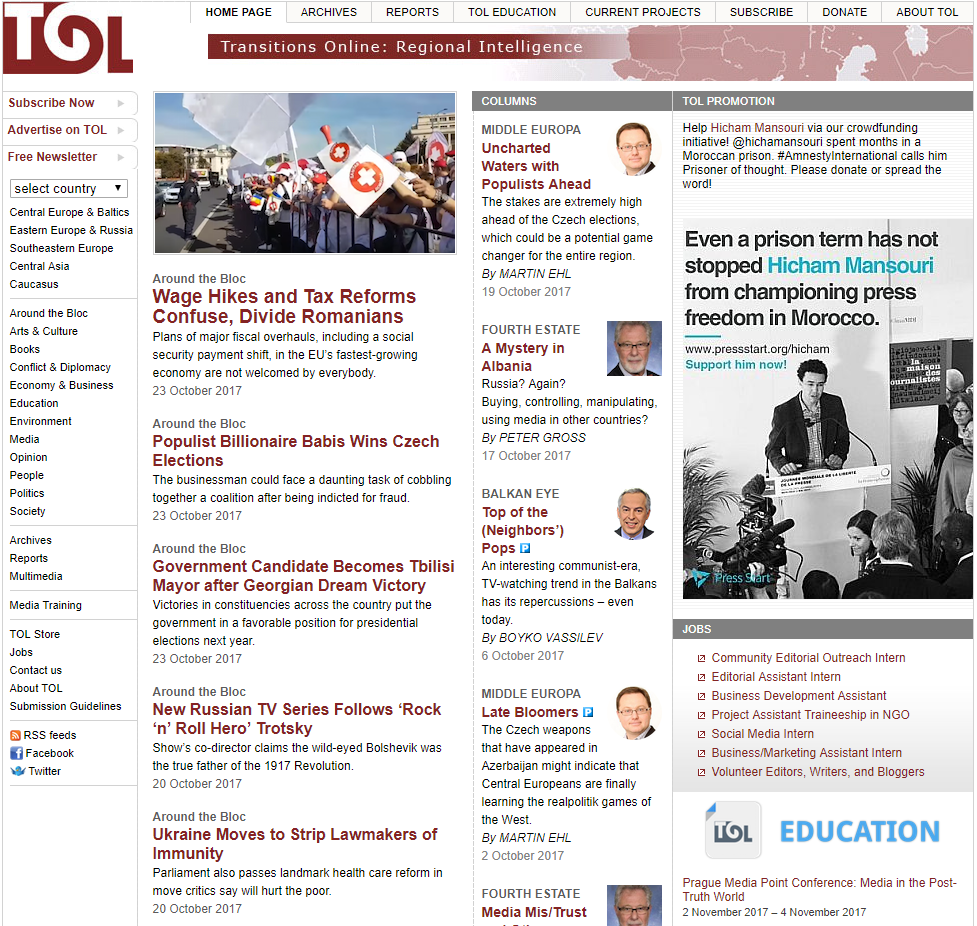
Plans of major fiscal overhauls, including a social security payment shift, in the EU’s fastest-growing economy are not welcomed by everybody.
More...
Private entrepreneurs are the driving force behind the country’s rising IT sector – but could they do it without the state at their back?
More...
Protests by senior citizens underline the parlous condition of retirees in Serbia and Bosnia.
More...
Decades in the making, Baku-Tbilisi-Kars could further isolate Armenia.
More...
A new law gives municipalities the power to exclude recipients of housing subsidies.
More...
Bosnia’s two entities cannot agree on route, placing political considerations above cost efficiency matters.
More...
A series of disputes with its neighbors has left Turkmenistan reliant on China to purchase its gas.
More...
Euros and dollars are beating out rubles in new remittance data, indicating a significant pattern shift.
More...
EU officials could consider the initiative at Eastern Partnership summit.
More...
Risk of poverty is high in Balkans, Baltics, and southern Europe, while Slovenia and Czech Republic are doing better.
More...
Time Warner-owned company dominates TV market across a wide swathe of Central and Eastern Europe.
More...
In the largest protests this fall, around 30,000 people expressed their discontent with several legislative proposals put forth by the Social Democrat coalition.
More...
The subject of the article is an analysis of the most important factors affecting the creation of investment demand by local government units in Poland. The first part defines investment demand through the prism of its origins in the public and private sectors. The types of investment demand characteristic of both the above mentioned sectors and the conditions for their formation are indicated. The second part analyzes the most important determinants of the creation of investment demand by local government units. The causes of specific trends of changes and trends in the share of property expenditures in total revenues of local government units in the years 1999-2015 were also presented. The main conclusions of the article were presented and the directions of the desired changes were presented.
More...
Government says that after years of promising to shutter a filthy power plant, real action is on the horizon.
More...
The aim of this article is to analyse the strategic goals of the energy policy of the Federal Republic of Germany. Key political motives behind Germany’s energy policy strategy The aim of this article is to analyse the strategic goals of the energy policy of the Federal Republic of Germany. Key political motives behind Germany’s energy policy strategy are reviewed, with the author applying the geo-economic approach. Noting that energy security and competitive economy of the Federal Republic of Germany rest on its energy partnerships with the Russian Federation, energy infrastructure and EU climate policy, the author reiterates the significance of stable political partnerships, determination to build a position as a distribution centre for energy and energy resources in Europe, as well as export of technology and imposition of national preferences on other countries. The American announcement of a renegotiation of the climate agreement may exert an unfavourable impact on the geo-economic interests of Germany in the area of energy.
More...
Around the middle of the current decade the EU’s division into the euro zone and states outside it has begun to consolidate. The states that had intended to join the zone have already done so, while the remaining ones are either not interested in joining or unable to make swift access. This situation now seems to have stabilised due to several factors, in particular the economic weakness of the euro area, the relatively high political and economic significance of countries outside the zone and hence their considerable influence on the EU, and the general stagnation of integration processes. However, it is becoming clearer in 2017 that the role of the above factors is dwindling, and this might transform relations between the euro area and the remaining Member States. Consequently, more dynamic enlargement of the single currency area and deeper divisions within the Union cannot be ruled out.
More...
A consistent growth of energy efficiency is one of the three pillars of Austria’s energy policy,alongside a development of renewable energy sources and a reduction of environmentallyhazardous emissions. Austrian policy aims at establishing a stable and effective energy systemthat guarantees secure energy supply, at the same time minimising environmental hazardswhile remaining economically efficient. Austria is a good example of a state that successfullyimplements energy efficiency measures, as it has the highest number of passive houses perresident in Europe and a sound policy on waste management. The text outlines the challengesfacing Austria with respect to energy efficiency and consumption reduction and examines thestrategies for the future, taking into account the country’s specific natural conditions.
More...
The author analyses fundamental concepts of the school of rational expectations (RATEX, an offspring of the Chicago school of economics). Theoretical foundations of the neoclassical macroeconomy are set out: the hypothesis of rational expectations in the circumstances of perfect competition and the principle of strategic interdependence. Central to that are the hypotheses of variants, misallocation of resources and neutrality of economic policy. Outlined are rent-seeking and direct unproductive profit-seeking as well as alternative models in the new theoretical economy: economic constitutionalism, deficitarians, the theory of political business cycles, supply side economics.
More...
The author, who sees himself primarily as a “longtime practitioner”, thinks that the government policies have failed to achieve national consensus and boost economy. In order to find a way out of the present situation, an agreement among the major political and economic forces is essential. In economy, the author - in accordance with the HSLS programme - advocates liberalization of exports, fast denationalization and restitution, a ban on further capitalization and the free granting of company shares, the traditional budgeting and cutting down on governement subsidies in economy.
More...